Forge
LIP6 Software
SAFE : Stochastic Arithmetic with Flexible Exponent
SAFE estimates rounding errors and detects numerical instabilities in programs using floating-point numbers with arbitrary mantissa-length and arbitrary exponent-length.
Project Leader : Fabienne JEZEQUEL
09/2024
QOSST : Quantum Open Software for Secure Transmissions
An open source suite to perform Continuous Variable Quantum Key Distribution.
Project Leader : Eleni Diamanti
04/2024
OMicroB : OCaml on Microcontroller Boards
OMicroB is a specialized implementation of the OCaml virtual machine designed to run on resource-constrained microcontrollers. This implementation can indeed run non-trivial OCaml programs on small microcontrollers, and provides the embedded software developer with all the high-level programming paradigms of the OCaml language (functional, imperative, modular, object-oriented) as well as increased security through static typing and automatic memory management. The OMicroB compilation chain takes a byte-code executable directly produced by the OCaml compiler and after several analysis passes (dead code detection, partial evaluation, ...) produces a C code embedding the VM, its execution library and the transformed byte-code. This produced C code, highly portable, targets different microcontroller architectures and can be compiled and executed on a standard PC for simulation and debugging purposes.
Project Leader : Emmanuel CHAILLOUX
04/2023
MQ Soft : A fast multivariate cryptography library
MQsoft is an efficient library in C for post-quantum multivariate-based cryptography. It includes HFE-based schemes such GeMSS, Gui and DualModeMS. Our library is modular and permits to perform fundamental arithmetic operations over finite fields: efficient constant-time arithmetic in GF(2^n), finding the roots of a univariate polynomial in GF(2^n)[X], evaluate efficiently multivariate quadratic systems in GF(2) (in constant-time and in variable-time), etc ...
Project Leader : Ludovic Perret
01/2023
PML : Polynomial Matrix Library
This library provides additions to NTL: efficient implementations for operations on univariate polynomial matrices and structured scalar matrices, and some uses of these for related algebraic computations. Work in progress includes adding functionalities (algebraic relations, normal form computation) and providing similar additions based on Flint.
Project Leader : Vincent Neiger
01/2023
HPDDM : high-performance unified framework for domain decomposition methods
HPDDM is a collection of preconditioners based on domain decomposition, either overlapping or non-overlapping. They can be used to solve large linear systems, as typically encountered when discretizing partial differential equations. These preconditioners can be used in conjunction with various Krylov methods. The library is usable in C, C++, Python, or Fortran codes.
Project Leader : Pierre JOLIVET
12/2022
msolve : Multivariate polynomial systems solving
msolve is a C library for solving multivariate polynomial systems. It relies on algebraic algorithms, in particular Gröbner bases. It allows the user to solve exactly polynomial systems with rational coefficients (real root isolation) and coefficients in a finite field (of cardinality < 2^31).
msolve provides high-performance implementations of algorithms which are known to be beyond the most efficient in this area. The library can be used through various computer algebra systems and is already integrated in OSCAR and SageMath.
msolve is developed in collaboration with Christian Eder (TU Kaiserslautern, Germany).
Project Leader : Mohab Safey El Din
10/2022
IOHprofiler : Iterative Optimization Heuristics Profiler
IOHprofiler, a benchmarking platform for evaluating the performance of iterative optimization heuristics (IOHs), e.g., Evolutionary Algorithms and Swarm-based Algorithms. See https://iohprofiler.github.io/ Licence:BSD-3
Project Leader : Carola Doerr
06/2021
SPY : SPY
SPY is a serious game designed to introduce players to the basics of computer programming. Through this project, we are working on a number of different issues: understanding the phenomena of computer learning; helping teachers to appropriate, design and script a serious game for learning computer programming; working on the accessibility of learning programming for students with special needs.
Project Leader : Mathieu Muratet
01/2021
ScenoClasse : ScenoClasse
ScenoClasse est un outil de scénarisation issu de la recherche et destiné aux enseignants. Il leur permet de préparer leurs séances autour de l’informatique/ la pensée informatique. ScenoClasse permet aux enseignants de créer, éditer, documenter et agencer des activités d’enseignement de la pensée informatique en scénarios puis de publier et d’exporter ces scénarios sous différents formats de sortie (fiche de préparation papier ou sur tablette/téléphone, diaporama, etc.). Ils peuvent également copier et adapter des scénarios créés par d’autres. Chaque scénario rendu public sur la plateforme ScenoClasse peut être enrichi collectivement par des commentaires et des retours d’expériences. Ces fonctionnalités ont été pensées pour permettre à un scénario d’avoir un cycle de vie au-delà du contexte prévu par son auteur.
Project Leader : Amel Yessad
01/2021
MUMPS : MUltifrontal Massively Parallel Sparse direct Solver
Solver for sparse linear systems. The collaboration between LIP6 and Mumps Tech deals with the use of mixed precision low rank compression, in the context of the CIFRE PhD thesis of M. Gerest funded by EDF.
Project Leader : Théo MARY
11/2020
AffApy : python library for multiprecision Affine Arithmetic
AffApy is a Python library for multiprecision Affine Arithmetic
Project Leader : Thibault HILAIRE
01/2020
CosyVerif : Software Environment for the Formal Specification and Verification of Dynamic Systems
CosyVerif is a software environment whose goal is the formal specification and verification of dynamic systems.
Project Leader : Fabrice KORDON
06/2019
PaInLeSS : PArallel INstantiabLE Sat Solver
PArallel INstantiabLE Sat Solver (Painless) is a framework written in C++ that simplifies the implementation and evaluation of new parallel SAT solvers for many-core environments. The components of Painless can be instantiated independently to produce a new complete solver. The guiding principle is to separate the technical components dedicated to some specific aspect of concurrent programming, from the components implementing heuristics and optimizations embedded in a parallel SAT solver.
Project Leader : Souheib Baarir
06/2019
BCMCyPhy : Component model for cyber-physical control systems
This research project and its associated software aim at designing and implementing a software component model for cyber-physical control systems. It develops over the BCM4Java project from which it uses the basic concepts and the implementation of distributed components in Java (10.000 lines of code and documentation today). Besides integrating real time components, this project studies component-based software architectures for control, their specification using stochastic hybrid systems and their simulation using models following the DEVS standard. A particular focus is given on the parallel composability between components, their individual specifications and simulation models. A software subproject of BCMCyPhy proposes a new implementation in Java of the DEVS standard for modular simulation of components and their assemblies (20.000 lines of code and documentation today). The simulators obtained through the composition of the components simulator models allow to debug, test, verify and validate applications. This software has been used by a few tens of students and is still being used in the context of the ALASCA master 2 course since 2018.
Project Leader : Jacques MALENFANT
06/2019
Cosy : Symmetry controller
Cosy is an efficient C++ library designed to dynamically break symmetries in SAT solving. It builds upon state-of-the-art SAT solvers by integrating a symmetry controller that works in tandem with the Conflict-Driven Clause Learning (CDCL) algorithm. Cosy can be interfaced with most CDCL solvers, offering flexibility and improved performance, especially in highly symmetric SAT problem instances. It is available under an open-source GPL v3 license.
Project Leader : Souheib Baarir
04/2018
Dedale aims to facilitate and improve the experimental evaluation conditions of MAS algorithms and to contribute to the progress of the field towards decentralised solutions able to deal with real-world situations. Dedale is dedicated to the study of multi-agents coordination, learning and decision-making problems under real-life hypotheses. Dedale offers open, dynamic, asynchronous and partially observable environments. It allows to tackle either cooperative or competitive exploration, patrolling, pickup and delivery, treasure(s) or agent(s) hunt problems with teams from one to dozens of heterogeneous agents in discrete or continuous environments. These strengths make Dedale able to become a unifying environment for both MAS research and teaching communities in their goal to work and evaluate their proposals under realistic hypotheses.
Project Leader : Cédric Herpson
03/2018
MOPSA analyzer : MOPSA Static Analyzer
MOPSA is a multi-language program verification software based on sound static analysis by abstract interpretation. It automatically infers invariants and detects, at compile time, the possible run-time errors. The analysis computes an interpretation of programs in a collection of reusable abstractions programmed in OCaml. Thanks to its modular conception, MOPSA can be easily extended in the set of properties and the set of analyzed languages. MOPSA currently supports significant subsets of the C and Python 3 languages. In C, MOPSA detects undefined behaviors as well invalid calls to the standard C library (specified in a dedicated modelization language). In Python, MOPSA, performs a type, value, and exception analysis.
Project Leader : Antoine Miné
03/2018
TSAR : TSAR (Tera-Scale ARchitecture)
Project Leader : Alain Greiner
09/2017
FiXiF : Reliable fixed-point implementation of linear signal processing (and control) algorithms
FiXiF is a suite of tools used to implement filters on embedded devices (usually DSP, micro-controllers, FPGA or ASIC) with finite-precision impact in minds (fixed- or floating-point arithmetic).
Project Leader : Thibault HILAIRE
08/2017
Wi-Fi Direct, also called Wi-Fi P2P, is a new communication mode in Wi-Fi networks, which allows nearby users to communicate directly without an infrastructure composing of access points. This project implements a simulation model for Wi-Fi Direct in the INET Framework of the OMNeT++ simulator. A new module, DuoHost, has been defined for the formation of a new Wi-Fi direct group or joining an existing one.
Project Leader : Thi Mai Trang NGUYEN
06/2017
TTK : Topology ToolKit
The Topology ToolKit (TTK) is an open-source library and software collection for topological data analysis and visualization. TTK can handle scalar data defined either on regular grids or triangulations, in 2D, 3D, or more. It provides a substantial collection of generic, efficient and robust implementations of key algorithms in topological data analysis.
Project Leader : Julien Tierny
04/2017
E-LearningScape : E-LearningScape
E-LearningScape est un Serious Escape Game sur le thème de la pédagogie. Ce jeu, soutenu par Sorbonne Université, est une adaptation du jeu LearningScape conçu par SAPIENS et le CRI. Nous travaillons sur la conception d'un module de suivi des actions du joueur, afin de générer en temps réel des aides contextualisées selon les difficultés rencontrées par les joueurs Les algorithmes que nous avons développés s'appuient sur une modélisation des énigmes du jeu à l'aide de réseaux de Petri, ce qui nous a amenés à concevoir un outil générique d'aide à la construction de ceux-ci. La démarche consiste à exprimer des liens entre des comportements génériques à l’aide d’un langage spécifique et de relations logiques. Ces expressions sont ensuite analysées pour générer automatiquement un réseau de Petri qui modélise tous les parcours possibles. Ce réseau est utilisé pour analyser le parcours du joueur et pour proposer des aides adaptées.
Project Leader : Mathieu Muratet
03/2017
HA-NFV : High Availability Virtual Network Function placement
A Decision Support System (DSS) with graphical interface for Virtual Network Function placement in multi-layer networks under availability objectives.
Project Leader : Stefano SECCI
01/2017
ULOOF : User-Level Online Offloading Framework
Android application framework allowing any mobile application to be decompiled and recompiled with mobile application method computation offloading features to a remote virtual machine cloning the device. Adaptive decision making allows to offload a method to the VM when computation-energy consumption trade-off is profitable.
Project Leader : Stefano SECCI et Rami LANGAR
01/2017
BUT4Reuse : Bottom-Up Technologies for Reuse
BUT4Reuse provides a unified framework for mining software artefact variants: Commonality and variability analysis, Feature identification, Feature location, Feature constraints discovery, Feature model synthesis, Reusable assets construction. It is easily extensible and currently supports several artefact types: Java, C, EMF Models, Textual files, File structures, JSON and CSV files, and much more.
Project Leader : Tewfik ZIADI
01/2017
Puck : Puck
Puck is an architecture refatoring tool for Java software, which allows developpers to detect and remove unwanted dependencies from code.They can plan their refactorings on dependency graphs and then apply their plans to code automatically. Puck is still a research prototype.
Project Leader : Mikal ZIANE
10/2016
FYFY : FamilY For unitY
FYFY (FamilY For unitY) is an Entity Component System framework (ECS) specially made for Unity. This project is an extension of Bruno Capdevilla doctoral works who design Genome framework in As3.
Project Leader : Mathieu MURATET
06/2016
SPRED : SPRing EDitor
SPRED is a level editor designed for the Spring engine used by Prog&Play
Project Leader : Mathieu MURATET
06/2016
MAGAM : Multi-Aspect Generic Adaptation Model
MAGAM is a Multi-Aspect (didactic, pedagogic, affective and motivational, gaming, etc.) Generic Adaptation Model based on matrix calculation that aims to adapt learning activities.
Project Leader : Vanda LUENGO et Baptiste MONTERRAT
03/2016
tryalgo : Basic and advanced algorithms and datastructures
This Python library implements various algorithms and data structures such as graph, string and computational geometry problems.
Proofs of correctness of these algorithms are available in the French language book: Programmation efficace - les 128 algorithmes qu’il faut avoir compris et codés en Python au cours de sa vie.
Project Leader : Christoph DÜRR
03/2016
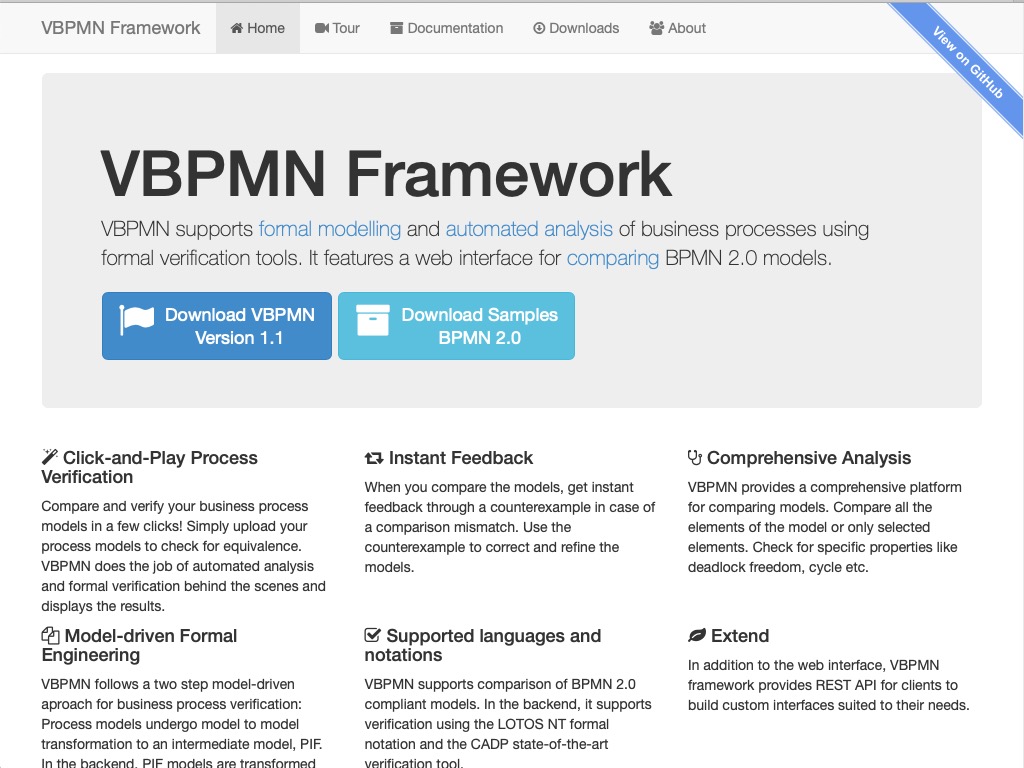
VBPMN : Framework for the Verification of BPMN processes
VBPMN supports formal modelling and automated analysis of business processes using formal verification tools. It features a web interface for comparing BPMN 2.0 models.
Project Leader : Pascal POIZAT
01/2016
LEA4PA : LEarning Analytics for Adaptation and Personnalisation
This project aims to built a plateform to assist teachers in adapting learning activities. Multiple indicators (cognitive, pedagogical, temporal, etc. will be inferred from data traces that are recorded and generated automatically or manually from the learner activities. Visualization systems will be proposed to assist teachers in their activities' adaptation process and make it.
Project Leader : Vanda LUENGO et Amel YESSAD
01/2016
MySlice v2 : Web portal to reserve and manage heterogeneous ICT resources from federated platforms
Web portal to reserve and manage heterogeneous ICT resources from federated platforms
Project Leader : Serge FDIDA
01/2016
F-Interop : Remote interoperability testing services for IoT devices
Remote interoperability testing services for IoT devices
Project Leader : Serge FDIDA
01/2016
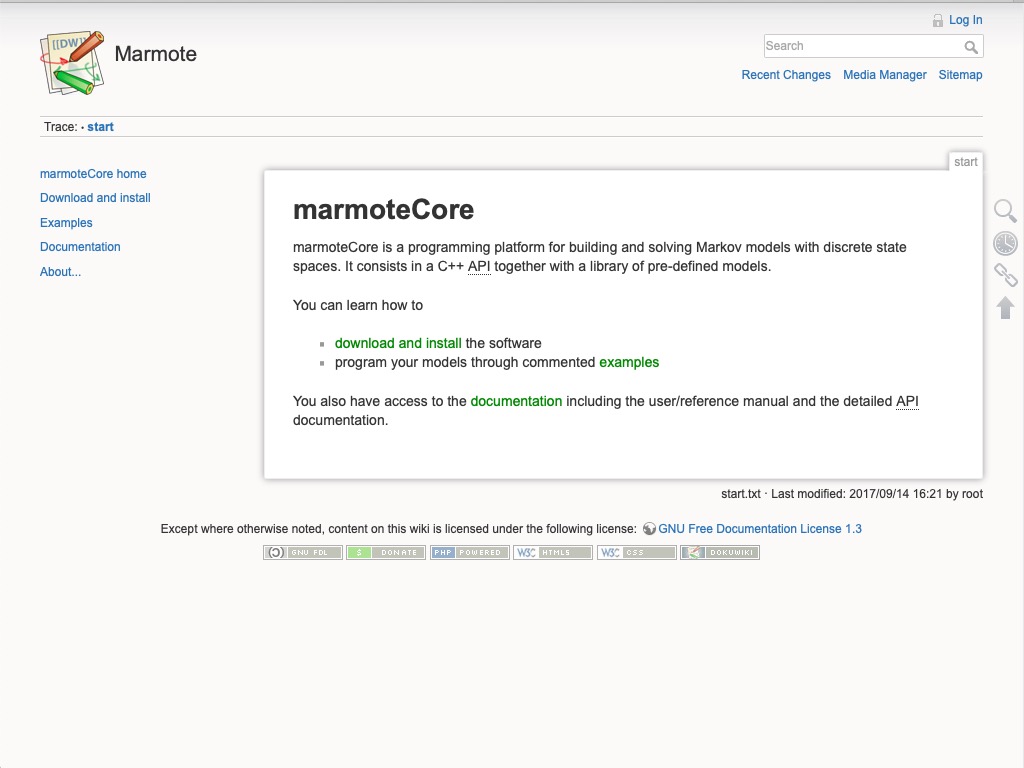
Marmote : A Markov Modeling Platform
Marmote is an open environment for modeling with Markov chains. This platform aims at providing the general scientific user with tools for creating Markov models and computing, or simulating, their behavior.
Project Leader : Emmanuel Hyon
01/2016
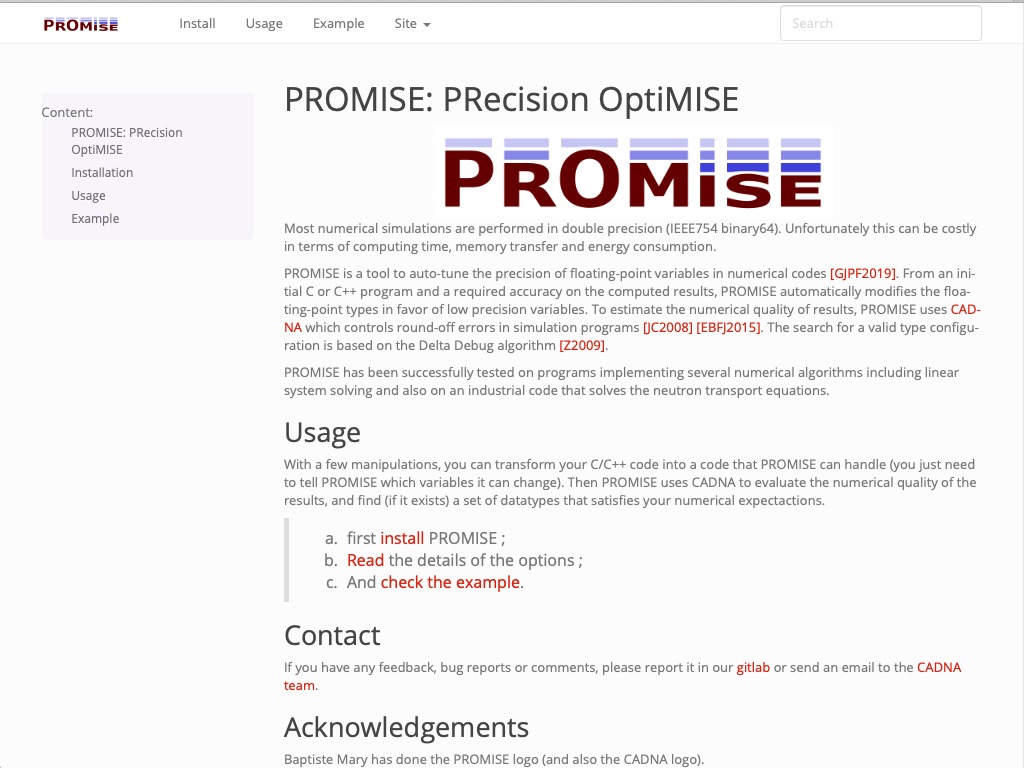
PROMISE : PRecision OptiMISE
PROMISE is a tool to auto-tune the precision of floating-point variables in numerical codes.
Project Leader : Fabienne JEZEQUEL
01/2016
piexplorer : an explicit state-space generation tool and a model-checker for the Pi-calculus
The problem of generating an explicit state-space for the pi-calculus is a complex problem. As of today, there exists only two tools with this functionality : the HAL laboratory and pi-explorer. The latter is based on a symbolic semantics that is much more economical than the early semantics as implemented by HAL. A model checker is also associated to the tool, but it is possible to use external tools based on the state graphs generated by the pi-explorer. These tools are based on recent works of the APR team (the pi-graphs), in a collaboration with university of Evry and université libre de Bruxelles.
Project Leader : Frédéric PESCHANSKI
09/2015
LaTTe : a laboratory of type theory experiments
LaTTe is a proof assistant library based on type theory. The specific feature of LaTTe is its design as a library (unlike most proof assistant, generally designed as standalone tools) tightly integrated with the Clojure language and ecosystem. This enables "proving in the large": sharing mathematical contents across the internet in a collaborative way. It also provides a domain specific language for declarative proofs, based on "fitch-style" proofs for natural deduction. The tool is developed by members of the APR team in a collaboration with the Whisper team (Pierre-Evariste Dagand).
Project Leader : Frédéric PESCHANSKI
03/2015
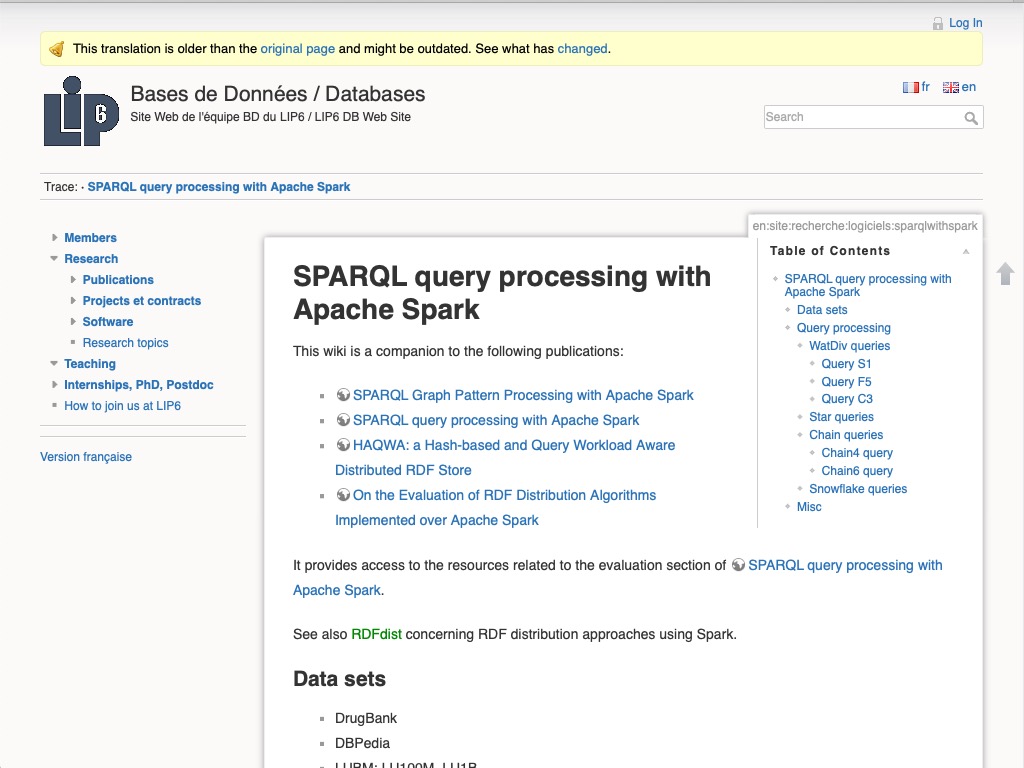
SPARQL on Spark : SPARQL query processing with Apache Spark
A common way to achieve scalability for processing SPARQL queries over large RDF data sets is to choose map-reduce frameworks like Hadoop or Spark. Processing complex SPARQL queries generating large join plans over distributed data partitions is a major challenge in these shared nothing architectures. In this article we are particularly interested in two representative distributed join algorithms, partitioned join and broadcast join, which are deployed in map-reduce frameworks for the evaluation of complex distributed graph pattern join plans. We compare five SPARQL graph pattern evaluation implementations on top of Apache Spark to illustrate the importance of cautiously choosing the physical data storage layer and of the possibility to use both join algorithms to take account of the existing predefined data partitionings. Our experimentations with different SPARQL benchmarks over real-world and synthetic workloads emphasize that hybrid join plans introduce more flexibility and often can achieve better performance than join plans using a single kind of join implementation.
Project Leader : Hubert NAACKE
01/2015
http://www-bd.lip6.fr/wiki/en/site/recherche/logiciels/sparqlwithspark
MOOC backend : Backend server handling network measurement requests coming from a MOOC
Backend server handling network measurement requests coming from a MOOC
Project Leader : Timur FRIEDMAN
01/2015
ITS-Tools : Instantiable Transition System Tools
ITS-tools is an easy to use and powerful award-winning model-checker supporting Safety, CTL and LTL properties for a variety of formalisms. It formally proves system correctness using exhaustive state space exploration.
Project Leader : Yann THIERRY-MIEG
01/2015
PENDULUM : OCaml syntax extension dedicated to the programming of reactive systems on the Web
Pendulum is a language dedicated to the programming of reactive systems on the Web. It has a powerful expressivity to describe synchronous concurrent systems communicating with broadcast signals. Its constructions and implementation are mostly based on Esterel. The language is embedded in OCaml as a syntax extension. It allows the programmer to describe reactive machines as OCaml values, and run them on signal arguments. The execution of concurrency in pendulum is completely sequential and the scheduling is static. (similar work and inspiration)
Project Leader : Rémy EL SIBAE
11/2014
Laalys : Laalys
Laalys (Learner Activity AnaLYser) is a software based on an approach that mixes expert driven and data driven approaches to describe players' behaviors in serious games. Pedagogical and semantic labels are inferred to describe the players' actions. The former version of Laalys was developped during P. Thomas PhD and was well adapted to case study serious games. The latest version of Laalys is adapted to highly interactive serious games with large state spaces.
Project Leader : Amel YESSAD et Mathieu MURATET
02/2014
ExBLAS : Exact Basic Linear Algebra Subprograms
ExBLAS aims at providing algorithms and implementations for fundamental linear algebra operations (like those included in the BLAS library) that deliver reproducible and accurate results with small or without losses to their performance on modern parallel architectures.
Project Leader : Stef GRAILLAT
01/2014
NFD : Named data network forwarder
NFD is a network forwarder that implements and evolves together with the Named Data Networking (NDN) protocol. The main design goal of NFD is to support diverse experimentation of NDN technology. The design emphasizes modularity and extensibility to allow easy experiments with new protocol features, algorithms, and applications. NFD is an open and free software package licensed under GPL 3.0 license and is the centerpiece of our committement to making NDN’s core technology open and free to all Internet users and developers.
Project Leader : Giovanni PAU
12/2013
VerChor : Framework for the Verification of Choreographies
VerChor enables you to design correct distributed systems following the choreography-based developement approach. Just model the system interaction protocol in your favorite language and let VerChor check for its realizability and retrieve peer interaction skeletons, or let it generate peer controllers to ensure the conformance to the system specification of a set of peers you want to reuse !
Project Leader : Pascal POIZAT
01/2013
CarFi : Enabling V2X with Wifi
CarFi enables a moving car to connect and communicate with existing WiFi infrastructures. CarFi has been designed to facilitate connected car services at a fraction of the cost. The software is PRIVATE and the ideas are protected by a patent application.
Project Leader : Giovanni PAU
01/2013
BCM4Java : Basic Component Model for Java
This project is an implementation of a distributed software component model in Java (20.000 lines of code and documentation today, under GitHub). It proposes the main concepts of the component-based approach: software components, component interface, ports exposing interfaces required and offered by components and explicit connectors. Using the Java RMI technology, it enables distributed programming thanks to de the deployment of components on several Java virtual machines (executing on several computers) and to calls between components through RMI. Started in the context of the ANR SALTY research project where it allowed to implement an application deploying 10.000 distributed components, this software has been used by several hundreds of students and is still being used first in the context of the ALASCA master 2 course since 2014 and in the context of the Components master 1 course since 2019.
Project Leader : Jacques MALENFANT
11/2012
SFA : API to federate platforms
API to federate platforms
Project Leader : Serge FDIDA
01/2012
BOM : Block-o-Matic!
Block-o-Matic is a web page segmentation algorithm based on an hybrid approach for scanned document segmentation and visual-based content segmentation. A web page is associated with three structures: the DOM tree, the content structure and the logical structure. The DOM tree represents the HTML elements of a page, the geometric structure organizes the content based on a category and its geometry and finally the logical structure is the result of mapping content structure on the basis of the human-perceptible meaning that conforms the blocks. The segmentation process is divided in three phases: analysis, understanding and reconstruction of a web page. An evaluation method is proposed in order to perform the evaluation of web page segmentations based on a ground truth of 400 pages classified into 16 categories. A set of metrics are presented based on geometric properties of blocks. Satisfactory results are reached when comparing to other algorithms following the same approach.
Project Leader : Andrès SANOJA
01/2012
AbSolute : AbSolute
AbSolute is a constraint solver based on abstract domains.
It implements the resolution method presented in the article: (VMCAI), Rome, Italy, 2013 [Article] [Article in French] Antoine Miné, Charlotte Truchet, Frédéric Benhamou, Constraint Solver based on Abstract Domains, 14th International Conference on Verification,
This solver can solve continuous, discrete and mixed problems (containing both integer and real variables) and proposes techniques for processing both linear and non-linear constraints. Rounding errors are taken into account during the resolution. The solver calculates sound float approximations of the real solutions of a problem. AbSolute uses Apron, an Ocaml library of abstract domains, which solves problems using other abstract domains than intervals.
Project Leader : Marie PELLEAU
11/2011
Arbogen : a fast uniform random tree generator
Arbogen is a fast uniform random generator of tree structures. The tool reads a grammar file describing a tree structure (e.g. binary trees, 2-3-4 trees, etc.) and a size interval (eg. trees of size 1000+-100). From the grammar one or many trees satisfying the structure and the size interval are produced. The generated tree are generated with a guarantee of uniformity, which means that it is the "average" tree for the given size. The tool relies on advanced algorithms based on Boltzman sampling, based on recent APR research works (in the realm of ANR Magnum 2010-2014).
Project Leader : Frédéric PESCHANSKI
10/2011
SPOC : Strem Processing with OCaml
SPOC is a set of tools for GPGPU programming with OCaml.
The SPOC library enables the detection and use of GPGPU devices with OCaml using Cuda and OpenCL. There is also a camlp4 syntax extension to handle external Cuda or OpenCL kernels, as well as a DSL (called Sarek) to express GPGPU kernels from the OCaml code.
Project Leader : Mathias BOURGOIN
09/2010
SAM : Stochastic Arithmetic in Multiprecision
The SAM library enables rounding error estimation in arbitrary precision programs.
Project Leader : Fabienne JEZEQUEL
01/2010
WiPal : IEEE 802.11 traces manipulation software
WiPal is a piece of software dedicated to IEEE 802.11 traces manipulation. It comes as a set of programs and a C++ library. A distinctive feature of WiPal is its merging tool, which enables merging multiple wireless traces into a unique global trace. This tool works offline on PCAP traces that do not need to be synchronized. WiPal also provides statistics extraction and anonymization tools, and its authors plan to extend it. WiPal’s key features are flexibility, ease of use, and efficiency.
Project Leader : Marcelo DIAS DE AMORIM
04/2009
Prog&Play : Prog&Play
Prog&Play is a library designed for Real Time Strategy games (RTS). It enables player to program easily and interactively units of the video game. Currently, Prog&Play is integrated into Kernel Panic, a multiplayer RTS. Prog&Play and Kernel Panic enable to design serious games for programming practice.
Project Leader : Mathieu MURATET
01/2008
WScout : Lightweight PCAP file visualizer.
WScout provides a PCAP traces visualizer that is able to work with huge traces (>10 GiB). Its goals are speed and low memory requirements. Despite its design being protocol-agnostic, it currently handles only Prism and IEEE 802.11 headers, hence its name.
Project Leader : Marcelo DIAS DE AMORIM
09/2007
Paris Traceroute : Paris Traceroute
Improved version of the classic tool for tracing routes in the internet
Project Leader : Timur FRIEDMAN
01/2006
PNML Framework is a prototype implementation of ISO/IEC-15909 part 2, International Standard on Petri Net Markup Language. The primary purpose of PNML is to enable interoperability among Petri net tools. PNML framework has thus been designed to back the Standard. It will enable Petri nets tools developers to seamlessly integrate PNML support into their tools. It provides an extensive and comprehensible API to create, save, load and browse PNML models.
Project Leader : Fabrice KORDON
04/2005
CORIOLIS : Platform for physical synthesis of integrated circuits
Coriolis is an experimental integrated platform for the research, development and evaluation of new back-end VLSI design flows. Interconnect scaling to nanometer processes presents many difficult challenges to CAD flows. Currently academic research on back-end tend to address only specific algorithmic issues separately, although one key issue to address is the cooperation of multiple algorithmic tools. CORIOLIS, our platform, is based on an integrated C++ database around which all tools consistently interact and collaborate. This platform currently includes a timing-driven global place and route flow.
Project Leader : Jean-Paul CHAPUT
01/2004
CAIRO : Analog IP Design
Our purpose is to provide a language for designing generators of analog functions, that can be easily ported to new set of specfications and new technologogy processes. We are currently developing such a language that is called CAIRO+
The CAIRO+ language supports the four steps of a design flow based on net-list and layout templates. This language is aimed to help the designer to capture his knowledge, thus creating a library of layout-aware analog functions. It is based on C++ language. The design flow relevant to CAIRO+ is the following :
->net-list and layout template capture, ->design space exploration (managing electrical constraints) ->shape function computation (managing geometrical constraints) ->layout generation (place and route) CAIRO+ allows creating complex hierarchical analog function generators by using existing generators of simpler functions. It is an answer to the problem of Analog and Mixed IPs.
As a demonstration of the CAIRO+'s capabilities, we are developping Analog to Digital converters, specially Sigma Delta.
Project Leader : Marie-Minerve LOUËRAT
01/2004
DDD : Library for manipulation of Data Decision Diagrams
libDDD is a package for manipulation of Data Decision Diagrams and Hierarchical Set Decision Diagrams. It supports flexible data types and "saturation" algorithms to offer cutting edge performances using decision diagrams. It is a C++ package distributed under Gnu LGPL.
Project Leader : Yann THIERRY-MIEG
01/2001
JADE : The Java Agent DEvelopment framework
JADE (Java Agent DEvelopment Framework) is an open source platform for peer-to-peer agent based applications.
JADE simplifies the implementation of multi-agent systems through a middleware that complies with the FIPA specifications for interoperable intelligent multi-agent systems.
JADE provides a simple yet powerful task execution and composition model, peer-to-peer agent communication based on asynchronous message passing, a yellow pages service supporting publish subscribe discovery mechanism and many other advanced features that facilitates the development of distributed systems.
A JADE-based system can be distributed across the internet and can tranparently deploy agents on Android and J2ME-CLDC MIDP 1.0 devices. The platform configuration as well as the agent number and locations can be changed at run-time, as and when required.
Project Leader : Cédric Herpson
01/2000
is a Petri Net based CASE environment. It offers a set of services to perform specification, validation, formal verification, model checking, compute structural properties (invariants, traps, syphons etc.) simulate and generate code. These services have been implemented either by members of our team or university partners (Technical university of Helsinki, University of Torino, Technical university of Munchen, Bell laboratories). The second geration of CPN-AMI, build on top of FrameKit, is available on the Internet since March 1997.
Project Leader : Fabrice KORDON
12/1994
Meroon is an Object-Oriented System written in Scheme.
Project Leader : Christian QUEINNEC
01/1993
CADNA : Control of Accuracy and Debugging for Numerical Application
CADNA is a library which allows to perform scientific computations with the estimation and the control of the round-off error propagation.
Project Leader : Fabienne JEZEQUEL
01/1992
Macao : Modélisation Analyse et Conception Assistées par Ordinateur
Macao is a generic graph drawing software that lets you create and manipulate graphs quickly and easily. It is an intuitive interface that enables to automates many of the time-consuming tasks involved in building graphs. Macao customization facilities enable the quick implementation of a new graph editor dedicated to a new type of graphical representation.This enable prototyping of new formalism, which is usefull when defining them. Macao can be considered as a standalone tool. However, it is a natural complement to FrameKit, a software platform dedicated to the prototyping and quick implementation of CASE environments.
Project Leader : Jean-Luc MOUNIER
09/1987
aGrUM : a Graphical Unified Model
aGrUM is a C++ library designed for easily manipulating graphical models. Its range of applications is quite large as it is designed, e.g., for performing learning tasks (for instance, learning Bayes nets from data), planning tasks (FMDPs) and inference (Bayes nets, GAI-nets, influence diagrams).
Project Leader : Christophe GONZALES & Pierre-Henri WUILLEMIN
WEB-R : Web-R, the complete memory of my Web
Web-R system, a non-intrusive and fast recording tool that performs a systematic and complete storage of user’s web pages and navigation.
Project Leader : Alain LIFCHITZ

RAGLib : A Library for Real Algebraic Geometry
This library, implemented in Maple, contains some functionalities for the study of real solutions of positive dimensional systems.
Project Leader : Mohab SAFET EL DIN
VideoScm2003 : VideoScm2003
Training software for learning recursive programmation in Scheme.
Project Leader : Maryse PELLETIER et Michele SORIA
http://www-ari.ufr-info-p6.jussieu.fr/RESSOURCES/cederoms.htm
Epsilon : Epsilon
Epsilon is a library of functions implemented in Maple and Java for polynomial elimination and decomposition with (geometric) applications. It has 8 modules and contains more than 70 functions.
Project Leader : Dongming WANG
DARX est une plate-forme d'exécution générique pour systèmes multi-agents développée conjointement entre l'équipe OASIS du LIP6 et SRC. DARX permet de fiabiliser par réplication les agents. Outre sa généricité, sa principale originalité est (1) la capacité à pouvoir changer dynamiquement de stratégies de réplication en fonction des contraintes applicatives et (2) son adaptation à la grande échelle en adoptant une architecture hiérarchique. DarX est implanté au-dessus de Java-RMI.
Project Leader : Pierre SENS
VVM : Virtual Virtual Machine
Le nombre toujours croissant de domaine d'application émergent entraîne un nombre croissant de solutions ad-hoc, rigides et faiblement interopérables. Nous proposons une plateforme pour la construction d'applications et d'environnement d'exécution flexibles et interopérables appellée la Machine Virtuelle Virtuelle. Plusieurs logiciels sont disponibles en libre sur Internet autour de la MVV: la RVM (Recursive Virtual Machine) le CCG (Compiler Compiler Generator) CCG a été notamment utilisé par le SUN Research Lab dans le cadre de la KVM.
Project Leader : Bertil FOLLIOT
SPOT : Spot Produces Our Traces
SPOT (Spot Produces Our Traces) est une bibliothèque de model-checking facilement extensible. À la différence des model-checkers existants, dont le mode opératoire est immuable, SPOT fournit des briques que l'utilisateur peut combiner entre elles pour réaliser un model-checker répondant à ses propres besoins. Une telle modularité permet d'expérimenter facilement différentes combinaisons, et facilite le développement de nouveaux algorithmes. D'autre part, cette bibliothèque est centrée autour d'un type d'automates particulier permettant d'exprimer les propriétés à vérifier de façon plus compacte, qui n'a jamais été utilisé dans un outil jusqu'à présent.
Project Leader : Denis POITRENAUD
LfP : Language for Prototyping
Il s'agit d'un langage de spécification de systèmes répartis à partir duquel nous travaillons pour générer automatiquement des spécifications formelles et des programmes. Le compilateur de ce langage a été écrit et intégré dans la plate-forme FrameKit (à coté de l'environnement CPN-AMI pour permettre un couplage et exploiter les outils de vérification). Ce langage et son compilateur sont à l'origine de notre participation dans le projet RNTL MORSE
Project Leader : Fabrice KORDON
Outil de programmation littéraire
Project Leader : Christian QUEINNEC
Serveur FTP
https://www-ftp.lip6.fr contact ftpmaint (at) nulllip6.fr